Ionospheric Scintillation Monitor
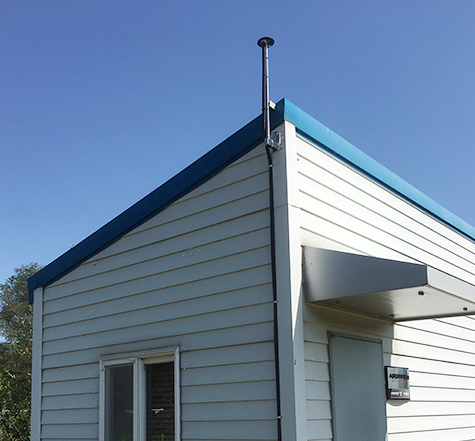
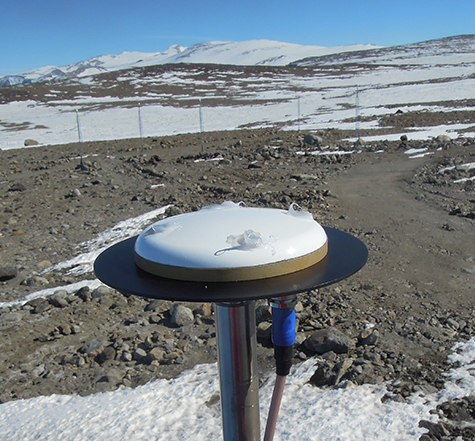
The ionospheric scintillation monitor observes scintillations, which are ionospheric irregularities, caused by a short time scale that cause satellite communication disturbance, radio wave attenuation and a large error in the position of navigation system. This instrument is composed of an antenna and a receiver that receives GPS signals. It observes changes in GPS signal strength in real time and measures GPS L1 and L2 signal phase scintillation indices (σφ) and GPS L1 and L2 signal amplitude scintillation indices (S4) and total electron contents (TEC). Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI) has been operating an ionospheric scintillation monitor at the Jangbogo Station in Antarctica since December 2015 to monitor real-time scintillation of the Antarctic ionosphere and to study the ionospheric irregularities of polar regions. In addition, since September 2016, KASI has been operating an ionospheric scintillation monitor at the VHF ionospheric radar observatory in the Gwangyangdae Air Force Base in order to investigate real-time ionospheric scintillation over the Korean Peninsula and ionospheric irregularities of the middle latitude.

|

|
|

|
||
| [ Ionospheric scintillation monitor at the VHF ionospheric radar observatory in the Gwangyangdae Air Force Base: GPS receiving antenna and receiver ] | ||

|

|
|

|
||
| [ Ionospheric scintillation monitor at the Jangbogo Station in Antarctica: GPS receiving antenna and receiver ] | ||
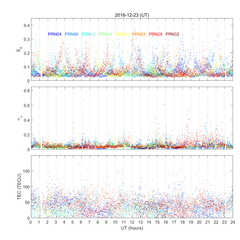
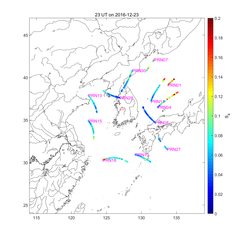
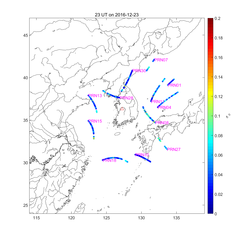
[ Gyeryong Ionospheric Scintillation Monitor data: (from left) Daily variation, S4 map, SIGH map ]
